In our increasingly digital world, the computer mouse has become an essential tool for navigating the vast landscape of technology. Whether you’re a seasoned user or just starting out, mastering the art of holding a computer mouse is crucial for efficient and comfortable computing. In this guide, we will delve into the fundamentals of holding a computer mouse, providing you with essential tips and techniques to enhance your productivity and reduce the risk of strain or discomfort. So, if you’re ready to take control of your digital experience, let’s dive into the world of proper mouse grip and discover the key to navigating the digital realm with ease and precision.
At first glance, holding a computer mouse may seem like a straightforward task. However, many people unknowingly adopt improper hand positions that can lead to fatigue, discomfort, and even long-term issues. By learning the correct grip and hand positioning techniques, you can maximize your control and accuracy while minimizing the strain on your hand and wrist. Whether you’re using a traditional wired mouse or a sleek wireless version, the principles of a proper grip remain the same. So, whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply someone looking to improve their computer skills, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to navigate the digital landscape with confidence and ease.
How to hold a computer mouse:
- Place your hand on the mouse, with your palm facing down.
- Your thumb should rest on the side of the mouse, and your fingers should arch over the top.
- Position your index and middle fingers on the left and right buttons respectively.
- Your ring finger and pinky can rest on the side of the mouse or on the mousepad.
- Adjust your grip to find a comfortable position that allows for precise movement.
How to Hold a Computer Mouse
The way you hold your computer mouse can greatly impact your productivity and comfort while using it. Whether you are a casual computer user or spend long hours working on your computer, it is important to hold the mouse correctly to avoid strain and discomfort. In this article, we will guide you through the steps of holding a computer mouse properly for optimal performance and comfort.
Step 1: Position your hand
The first step in holding a computer mouse correctly is to position your hand in a comfortable and natural way. Place your hand on the mouse, with your palm resting comfortably on the back of the mouse. Your fingers should naturally rest on the buttons and scroll wheel. Avoid gripping the mouse too tightly, as this can lead to muscle tension and fatigue over time.
It is important to note that there are different types of computer mice available, such as ergonomic mice or vertical mice, which may require a slightly different hand position. If you are using one of these specialized mice, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for hand placement and adjust accordingly.
Step 2: Maintain a relaxed grip
Once your hand is in position, it is important to maintain a relaxed grip on the mouse. Avoid squeezing the mouse too tightly or using excessive force when clicking. Instead, use a gentle and controlled pressure to click the mouse buttons. This will help prevent strain on your fingers and hand muscles.
Additionally, make sure your wrist is in a neutral position. Avoid bending your wrist too much or resting it on the desk while using the mouse. This can lead to discomfort and even repetitive strain injuries. Instead, keep your wrist straight and allow it to move naturally as you navigate the mouse.
Step 3: Move the mouse with your arm
When moving the mouse, use your entire arm rather than just your wrist. This will help distribute the movement and reduce strain on your wrist and fingers. Use smooth and controlled movements to navigate the cursor on the screen. Avoid making sudden or jerky movements, as this can lead to inaccuracy and discomfort.
If you find yourself frequently lifting the mouse to reposition it, consider adjusting the sensitivity settings of your mouse. Higher sensitivity can allow for smaller movements and reduce the need to lift the mouse frequently. Experiment with different sensitivity levels until you find one that suits your needs.
Step 4: Take regular breaks
Lastly, it is important to take regular breaks when using the computer mouse for extended periods. Even with the correct hand position and grip, prolonged use can still lead to muscle fatigue and discomfort. Take short breaks every 30 minutes to stretch your fingers, hands, and arms. This will help prevent stiffness and promote blood circulation.
In conclusion, holding a computer mouse correctly is essential for comfort and productivity. Remember to position your hand properly, maintain a relaxed grip, move the mouse with your arm, and take regular breaks. By following these steps, you can reduce the risk of strain and discomfort while using a computer mouse. Enjoy a more comfortable and efficient computing experience!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about how to hold a computer mouse:
1. How should I hold a computer mouse for optimal comfort and control?
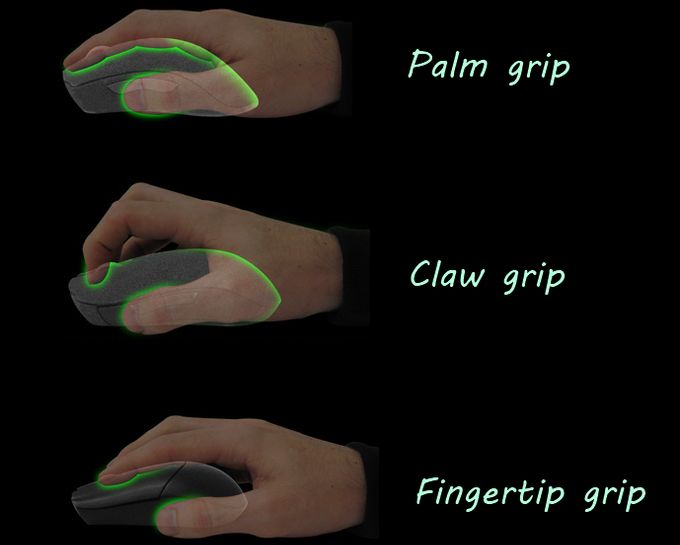
When holding a computer mouse, it is important to find a grip that is comfortable for you and allows for precise control. One common grip is the palm grip, where you rest your entire hand on the mouse with your fingers extended over the buttons. Another grip is the claw grip, where your palm rests on the back of the mouse and your fingers are arched over the buttons. Choose a grip that feels natural and doesn’t strain your hand or fingers.
It is also important to position the mouse in a way that allows your wrist to remain in a neutral position. Avoid bending your wrist too much or resting it on the desk, as this can lead to discomfort and potential injuries over time. Instead, keep your wrist straight and let it glide smoothly as you move the mouse.
2. How do I adjust the sensitivity of my mouse?
To adjust the sensitivity of your mouse, you can usually find the settings in your computer’s operating system or in the mouse software that came with your device. Look for options related to “mouse sensitivity” or “tracking speed.” Increasing the sensitivity will make the cursor move faster, while decreasing it will make it move slower. Experiment with different sensitivity levels to find the one that suits your needs and feels comfortable to use.
Keep in mind that the ideal sensitivity may vary depending on the tasks you are performing. For tasks that require precision, such as graphic design or photo editing, a lower sensitivity may be preferable. On the other hand, for tasks that require quick movements, like gaming or navigating large documents, a higher sensitivity can be beneficial.
3. Should I use my wrist or arm to move the mouse?
When moving the mouse, it is generally recommended to use a combination of wrist and arm movements. Using only your wrist can lead to strain and repetitive motion injuries, while using only your arm may result in less precise control. By combining both movements, you can achieve a balance between comfort and accuracy.
For small movements, such as clicking on icons or buttons, it is sufficient to use your wrist. However, for larger movements, like moving the cursor across the screen, involve your arm as well. This not only reduces strain on your wrist but also allows for smoother and more fluid mouse movements.
4. How can I prevent my hand from getting tired while using the mouse for long periods?
Using a computer mouse for extended periods can cause fatigue and discomfort in your hand. To prevent this, take regular breaks and stretch your fingers, wrist, and arm. Consider using an ergonomic mouse that is designed to provide better support and reduce strain on your hand and fingers.
Additionally, ensure that your workstation is set up ergonomically. Position your mouse within easy reach, so you don’t have to extend your arm or strain your shoulder. Use a mouse pad with a cushioned wrist rest to support your wrist and maintain a neutral position. Taking these precautions can significantly reduce the risk of hand fatigue and discomfort.
5. Are there any exercises or stretches I can do to alleviate mouse-related hand and wrist discomfort?
Yes, there are exercises and stretches you can do to alleviate hand and wrist discomfort caused by prolonged mouse use. One simple stretch is to extend your arm in front of you with your palm facing up, then gently pull back your fingers with the other hand until you feel a stretch in your forearm and fingers. Hold the stretch for a few seconds and repeat on the other hand.
You can also perform wrist rotations by extending your arm with the palm facing down and rotating your wrist in a circular motion. Another exercise is to make a fist and then spread your fingers wide, repeating this movement several times. These exercises help to improve blood circulation and flexibility in your hands and wrists, reducing the risk of discomfort and stiffness.
Using the Mouse Part 4 | Mouse Pointer | How to hold a Mouse Properly | Chapter 4 | Class 1 |
In conclusion, mastering the art of holding a computer mouse is not only crucial for efficient navigation but also for preventing discomfort and potential injuries. By following the proper technique, users can enhance their productivity while minimizing the risk of repetitive strain injuries. Remember to maintain a relaxed grip, position the mouse within easy reach, and utilize the support of a mouse pad or wrist rest for added comfort. With practice and awareness, individuals can transform their mouse-handling skills into a seamless and effortless experience.
Furthermore, as technology continues to evolve and become a staple in our daily lives, it is essential to adapt and learn how to navigate the digital world effectively. Holding a computer mouse may seem like a simple task, but it is one that can greatly impact our overall computing experience. By using the correct grip and positioning, users can not only enhance their accuracy and speed but also reduce the strain on their wrists and hands. So, let us all take the time to master this fundamental skill and unlock the full potential of our digital endeavors.

